Spring Beans are Java Objects or Instances which will be created and managed by Spring IOC/DI container.
Below is the lifecycle of Spring Beans
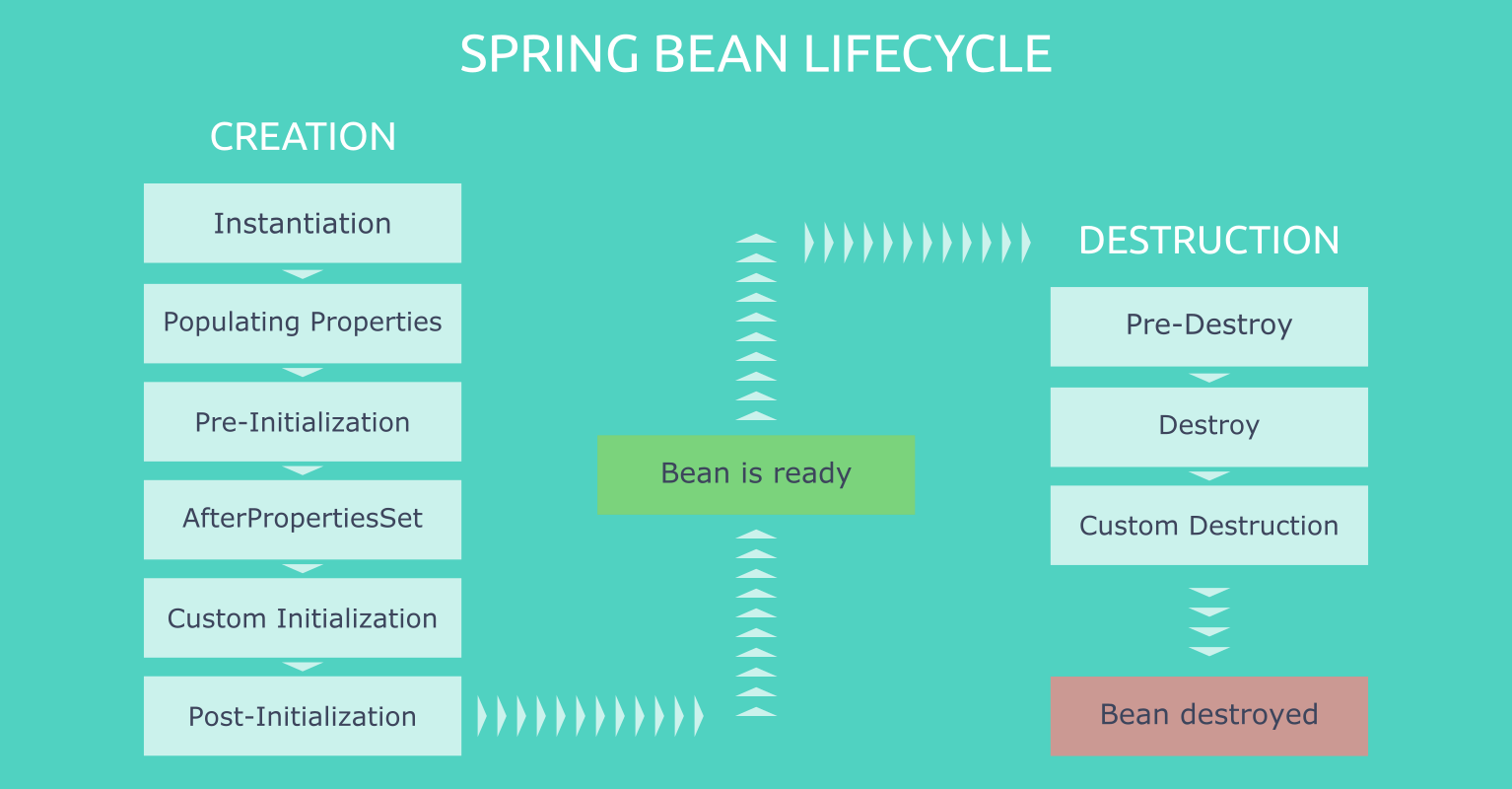
- 1. Bean Definition
Spring Bean will be defined using stereotype annotations or XML Bean configurations. - 2. Bean Creation and Instantiate
As soon as bean created and It will be instantiated and loaded intoApplicationContextandJVMmemory. - 3. Populating Bean properties
Spring container will create a beanid,scope,default valuesbased on the bean definition. - 4. Post-initialization
Spring provides Aware interfaces to access application bean meta-data details and callback methods to hook into the bean life cycle to execute custom application-specific logic. - 5. Ready to Serve
Now, Bean is created and injected all the dependencies and should be executed all the Aware and callback methods implementation. Bean is ready to serve. - 6. Pre-destroy
Spring provides callback methods to execute custom application-specific logic and clean-ups before destroying a bean fromApplicationContext. - 7. Bean Destroyed
Bean will be removed or destroyed from andJVMmemory.
Using Spring @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotations
The @PostConstruct annotation is used on a method that needs to be executed after dependency injection is done to perform any initialization. You can use annotation @PostConstruct for setup configuration before initializing bean.
The @PreDestroy annotation is used on methods as a callback notification to signal that the instance is in the process of being removed by the container. You can use @PreDestroy annotation for release memory after bean has finished processing.
package com.learncode24h.lifecycle.spring;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MailService {
private Map<String, String> map=null;
public MailService() {
map=new HashMap<>();
}
public void send(String mailTo){
System.out.println("Send email to - " + mailTo + "success");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
map.put("host", "mail.example.com");
map.put("port", "25");
map.put("from", "admin@abc.com");
System.out.println("Init config email " + map);
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
map.clear();
System.out.println("Release memory");
}
}
package com.learncode24h.lifecycle.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.learncode24h.lifecycle.spring")
public class AppConfig {
}
@ComponentScan annotation scans all beans, whose class is annotated by the @Componentannotation in a package, specified bybasePackages attribute.
package com.learncode24h.lifecycle.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// Send mail 1
MailService mailService1 = context.getBean(MailService.class);
mailService1.send("contact@learncode24h.com);
// Send mail 2
MailService mailService2 = context.getBean(MailService.class);
mailService2.send("admin@learncode24h.com");
context.close();
}
}
Result printed
Init config mail- {port=25, host=mail.example.com, from=admin@abc.com}
Send email to - contact@learncode24h.com
Send email to - admin@learncode24h.com
Release memory

