Loops in Java are designed to perform a specific task repeatedly. . In Java we have three types of basic loops: for, while and do-while.
The for and while statements perform the repetition declared in their body zero or more times until loop condition isn’t match (return false), then it will break from loop.
The do…while loop: it executes the statements within its body first then compare condition in while and repeatedly zero or more times until condition in while return false.
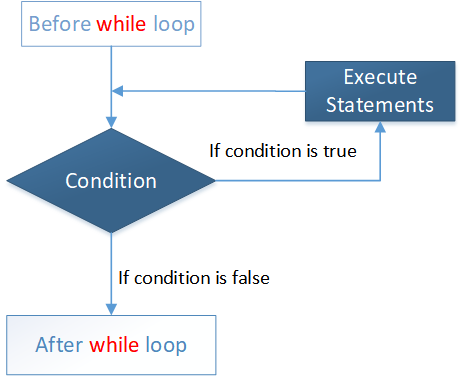
While Loops
The while loop is used to repeat a statement or block of statements as long as a particular condition is true. while loops look like this:
while (condition) {
bodyOfLoop;
}
The condition is a boolean expression. If it returns true, the while loop executes the statements in bodyOfLoop and then tests the condition again, repeating until the condition is false.
while ((ch != "\\") && (ch != "\t") && (ch != "\n") && (ch != "\r")) {
addChar(ch, theName);
ch = instream.read();
}
do…while Loops
The do loop is just like a while loop, except that do executes a given statement or block until a
condition is false. The main difference is that while loops test the condition before looping,
making it possible that the body of the loop will never execute if the condition is false the first
time it is tested.
do {
bodyOfLoop;
} while (condition);
For example:
int x = 1;
do {
System.out.println("Looping, round" + x);
x++;
} while (x <= 10);
Output:
Looping, round 1
Looping, round 2
Looping, round 3
Looping, round 4
Looping, round 5
Looping, round 6
Looping, round 7
Looping, round 8
Looping, round 9
Looping, round 10
For loop
for (initialization; test; increment) {
statements;
}
The start of the for loop has three parts:
– initialization is an expression that initializes the start of the loop. If you have a loop
index, this expression might declare and initialize it, for example, int i = 0. Variables
that you declare in this part of the for loop are local to the loop itself; they cease
existing after the loop is finished executing. (This is different from C or C++.)
– test is the test that occurs after each pass of the loop. The test must be a boolean
expression or function that returns a boolean value, for example, i < 10. If the test is
true, the loop executes. Once the test is false, the loop stops executing.
– increment is any expression or function call. Commonly, the increment is used to
change the value of the loop index to bring the state of the loop closer to returning
false and completing.
For example:
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i) {
System.out.println("Line " + i);
}
Output:
Line 1
Line 2
Line 3
Line 4
Line 5
Line 6
Line 7
Line 8
Line 9
Line 10
Breaking out of loop
In all the loops (for, while, and do), the loop ends when the condition you are testing for is met.
What happens if something odd occurs within the body of the loop and you want to exit the loop
early? For that, you can use the break and continue keywords.
break: it immediately halts execution of the current loop
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
//breaking the loop
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
Output:
1
2
3
4
continue: is used to continue the loop. It continues the current flow of the program and skips the remaining code at the specified condition. In case of an inner loop, it continues the inner loop only.
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
//using continue statement
continue;//it will skip the rest statement
}
System.out.println(i);
}
Output:
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
Enhanced FOR Loop
for(type VARIABLE: COLLECTION)
{
//Statements with VARIABLE
}
We must declare a VARIABLE of the same data type as the type of elements of the COLLECTION. Data type can Primitive like int, char, byte… or a Object type. There is NO CONDITION part in this enhanced for loop or for-each loop. By default, it works from the first element to the last element (fetch all elemtents from start to the end).